序
自己的数据结构与算法基础比较薄弱,现在也在刷AcWing,感觉比较乏力(最近动规刷的比较多,想吐,有点高屋建瓴,基础不牢)所以打算基础和提高一起抓,现在在刷的有AcWing、剑指Offer,之后看一下要不要LeetCode的基础。
2023年10月4日
JZ6 从尾到头打印链表
描述
输入一个链表的头节点,按链表从尾到头的顺序返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
如输入$\lbrace 1,2,3 \rbrace$的链表如下图:
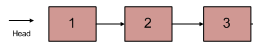
返回一个数组为$[3,2,1]$
$0 \le length \le 10000$
题解
递归
使用递归的方式可以从尾到头
递归的三个条件:
- 终止条件:递归进入链表尾
- 返回值:每次返回子问题之后的全部输出
- 本级任务:递归进入下一级,下一级数组返回时将本级节点添加在返回值的末尾
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
#include <cstddef>
class Solution {
public:
void recursion(ListNode* head,vector<int>& res){
if(head){
recursion(head->next,res);
res.push_back(head->val);
}
}
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
recursion(head,res);
return res;
}
};栈
将链表的每一元素压栈,将栈顶元素添入数组,栈顶出栈,交换链表顺序
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
#include <cstddef>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
stack<int> s;
while(head){
s.push(head->val);
head=head->next;
}
while(!s.empty()){
res.push_back(s.top());
s.pop();
}
return res;
}
};JZ24 反转链表
描述
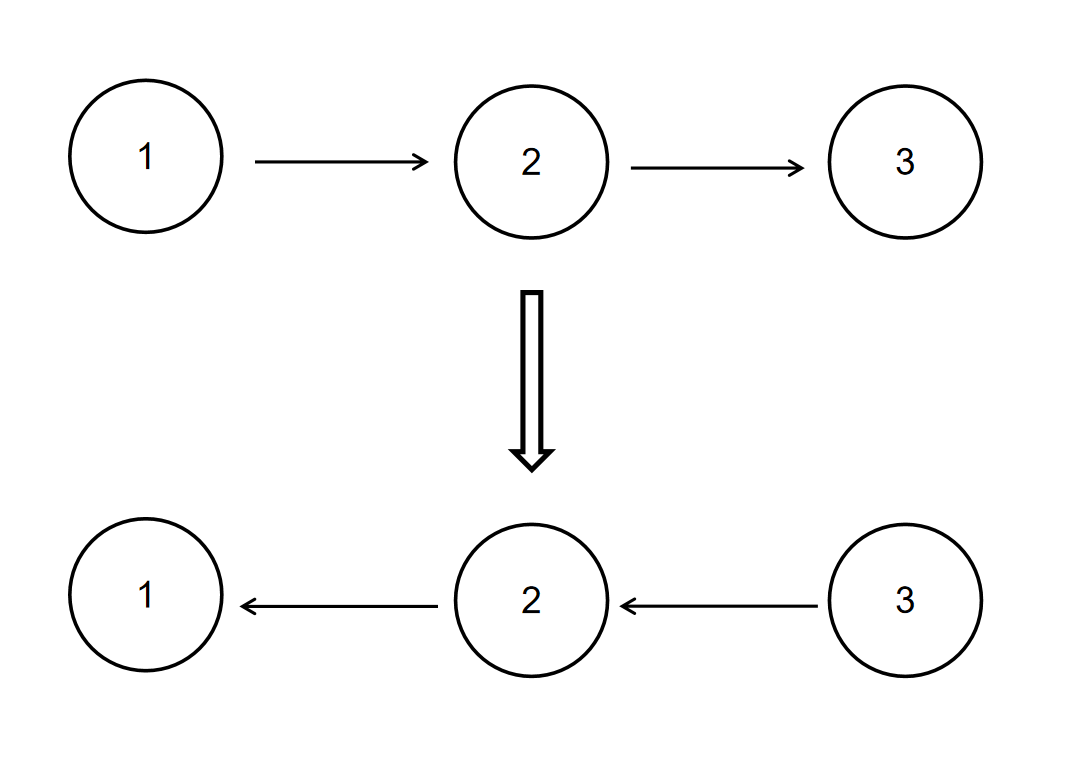
给定一个单链表的头结点pHead(该头节点是有值的,比如在下图,它的val是1),长度为n,反转该链表后,返回新链表的表头。
数据范围: $0 \le n \le 1000$
要求:空间复杂度$O(1)$,时间复杂度$O(n)$。
如当输入链表$\lbrace 1,2,3 \rbrace$时,
经反转后,原链表变为$\lbrace 3,2,1 \rbrace$,所以对应的输出为$\lbrace 3,2,1 \rbrace$。
以上转换过程如下图所示:
题解
递归
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
#include <cstddef>
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL){
return head;
}
ListNode* reverse=ReverseList(head->next);
head->next->next=head;
head->next=NULL;
return reverse;
}
};栈
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
#include <cstddef>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL){
return head;
}
stack<ListNode*> s;
while(head){
s.push(head);
head=head->next;
}
ListNode* node=s.top();
ListNode* reverse=node;
s.pop();
while(!s.empty()){
ListNode* tmp=s.top();
s.pop();
node->next=tmp;
node=node->next;
}
node->next=NULL;
return reverse;
}
};上面两种都是常规做法,非递归就用栈,需要注意的是栈最后需要在链表结尾添加NULL,否则会成环导致陷入死循环。
双链表
双链表的做法是比较巧妙的,构建一个新链表,然后遍历原链表的元素,对于每一元素尾插入新链表,最后返回的新链表就是反转链表。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
#include <cstddef>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
ListNode* reverse=NULL;
while(head){
ListNode* tmp=head->next;
head->next=reverse;
reverse=head;
head=tmp;
}
return reverse;
}
};双链表法的性能也是最好的
JZ25 合并排序链表
描述
输入两个递增的链表,单个链表的长度为n,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
数据范围: $0 \le n \le 10000$,$−1000 \le 节点值 \le 1000$
要求:空间复杂度 $O(1)$,时间复杂度$O(n)$
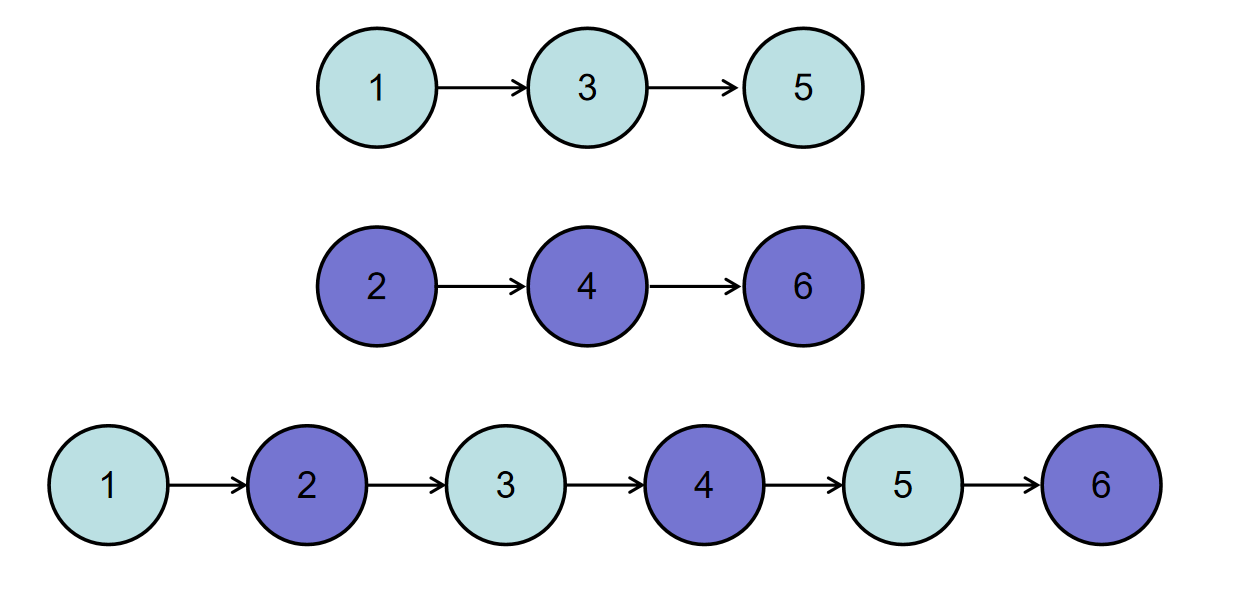
如输入{1,3,5},{2,4,6}时,合并后的链表为{1,2,3,4,5,6},所以对应的输出为{1,2,3,4,5,6},转换过程如下图所示:
题解
递归
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead1 ListNode类
* @param pHead2 ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
// write code here
if(pHead1==NULL){
return pHead2;
}
if(pHead2==NULL){
return pHead1;
}
if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){
pHead1->next=Merge(pHead1->next,pHead2);
return pHead1;
}else{
pHead2->next=Merge(pHead1,pHead2->next);
return pHead2;
}
}
};迭代
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead1 ListNode类
* @param pHead2 ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
// write code here
if(pHead1==NULL){
return pHead2;
}
if(pHead2==NULL){
return pHead1;
}
ListNode* res=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* node=res;
while(pHead1&&pHead2){
if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){
node->next=pHead1;
pHead1=pHead1->next;
}else{
node->next=pHead2;
pHead2=pHead2->next;
}
node=node->next;
}
if(pHead1){
node->next=pHead1;
}else{
node->next=pHead2;
}
return res->next;
}
};JZ52 两个链表的第一个公共结点
描述
输入两个无环的单向链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点,如果没有公共节点则返回空。(注意因为传入数据是链表,所以错误测试数据的提示是用其他方式显示的,保证传入数据是正确的)
数据范围: $n \le 1000$
要求:空间复杂度$O(1)$,时间复杂度$O(n)$
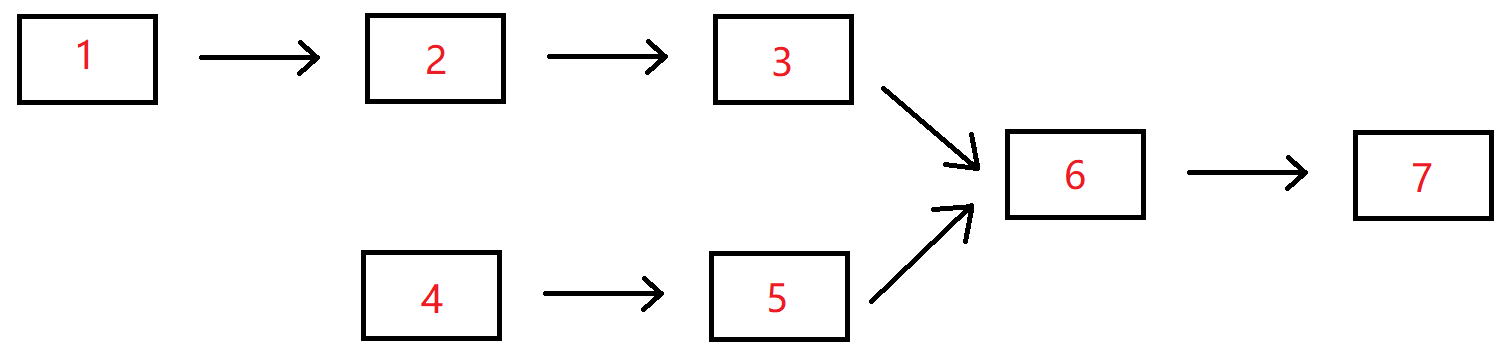
例如,输入{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7}时,两个无环的单向链表的结构如下图所示:
题解
双结点
第一个结点从第一个链表头开始遍历,遍历完后切换到第二个链表头;第二个结点反之。
两个结点遍历最终一定能够找到公共结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode* l1=pHead1,* l2=pHead2;
while(l1!=l2){
l1=(l1==NULL)?pHead2:l1->next;
l2=(l2==NULL)?pHead1:l2->next;
}
return l1;
}
};删减结点法
获取两链表的长度,将较长的链表删至与较短的链表长度一样,然后开始遍历至公共结点。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode* l1=pHead1,* l2=pHead2;
int len1=length(pHead1),len2=length(pHead2);
while(len1!=len2){
if(len1>len2){
l1=l1->next;
len1--;
}else{
l2=l2->next;
len2--;
}
}
while(l1!=l2){
l1=l1->next;
l2=l2->next;
}
return l1;
}
int length(ListNode* head){
int length=0;
ListNode* cur=head;
while(cur){
length++;
cur=cur->next;
}
return length;
}
};JZ22 链表中倒数最后k个结点
描述
给一个长度为n链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,返回null。
数据范围: $n \le 10000$,1<=结点值<=10000
要求:空间复杂度 $O(1)$,时间复杂度 $O(n)$
例如,输入{1,2},{3,4,5}时,对应的环形链表如下图所示:
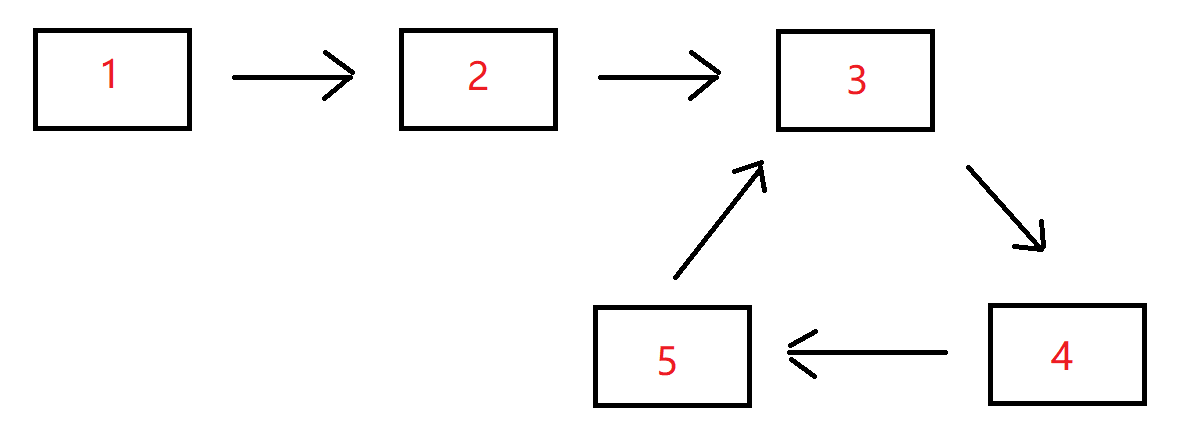
可以看到环的入口结点的结点值为3,所以返回结点值为3的结点。
题解
hash
使用hash键值对一一对应,不允许有重复,重复点为环的起点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
#include <unordered_set>
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==NULL) return NULL;
unordered_set<ListNode*> set;
while(pHead){
if(set.find(pHead)!=set.end()){
return pHead;
}
set.insert(pHead);
pHead=pHead->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};双指针
使用快慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,如果有环最终肯定会相遇,从相遇处到入口结点的距离与头结点与入口结点的距离相同
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==NULL) return NULL;
ListNode* l1=pHead,* l2=pHead;
while(l1!=NULL&&l1->next!=NULL){
l1=l1->next->next;
l2=l2->next;
if(l1==l2) break;
}
if(l1==NULL||l1->next==NULL) return NULL;
l1=pHead;
while(l1!=l2){
l1=l1->next;
l2=l2->next;
}
return l1;
}
};JZ22 链表中倒数最后k个结点
描述
输入一个长度为n的链表,设链表中的元素的值为$a_i$ ,返回该链表中倒数第k个节点。
如果该链表长度小于k,请返回一个长度为0的链表。
例如输入{1,2,3,4,5},2时,对应的链表结构如下图所示:
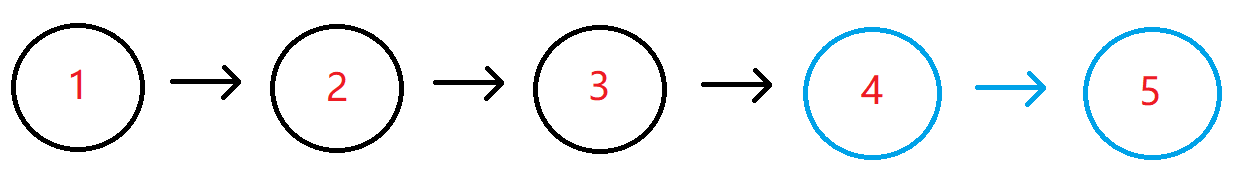
其中蓝色部分为该链表的最后2个结点,所以返回倒数第2个结点(也即结点值为4的结点)即可,系统会打印后面所有的节点来比较。
题解
长度法
疯狂遍历,先遍历出长度,然后将倒数改为正数
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
int len(ListNode* pHead){
ListNode* l=pHead;
int len=0;
while(l){
len++;
l=l->next;
}
return len;
}
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {
// write code here
int length=len(pHead);
if(length<k || k==0) return NULL;
int n=length-k;
while(n--){
pHead=pHead->next;
}
return pHead;
}
};栈
用栈很好想到,就是空间比较浪费
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {
// write code here
stack<ListNode*> s;
while(pHead){
s.push(pHead);
pHead=pHead->next;
}
ListNode* res=NULL;
while(k--){
if(s.empty()) return NULL;
res=s.top();
s.pop();
}
return res;
}
};快慢指针
连续两道用到快慢指针,这里的快慢指针有点类似于前面的长度法
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {
// write code here
ListNode* fast=pHead,* slow=pHead;
if(k==0) return NULL;
while(k--){
if(fast==NULL) return NULL;
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};To Be Continued



